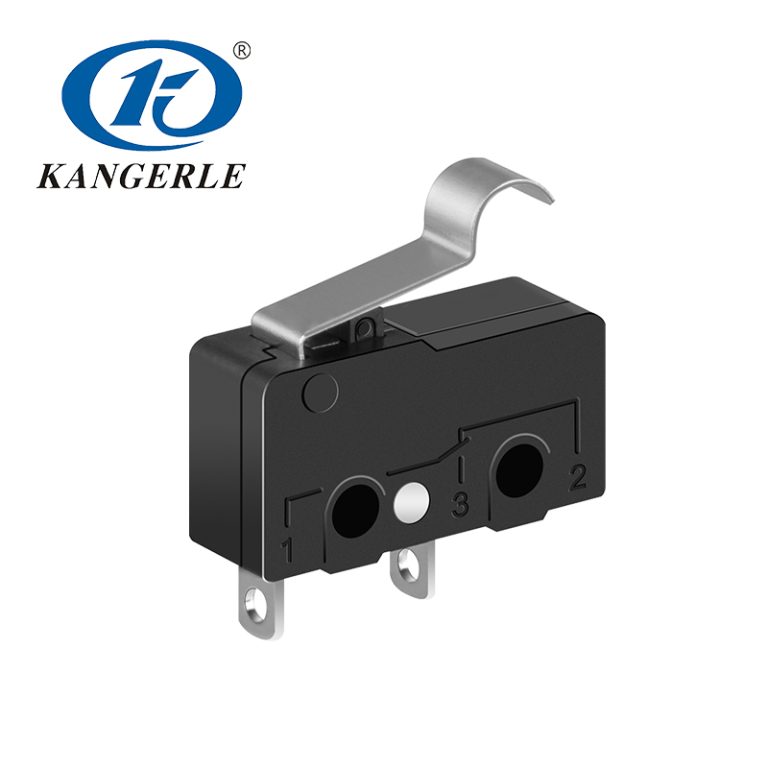
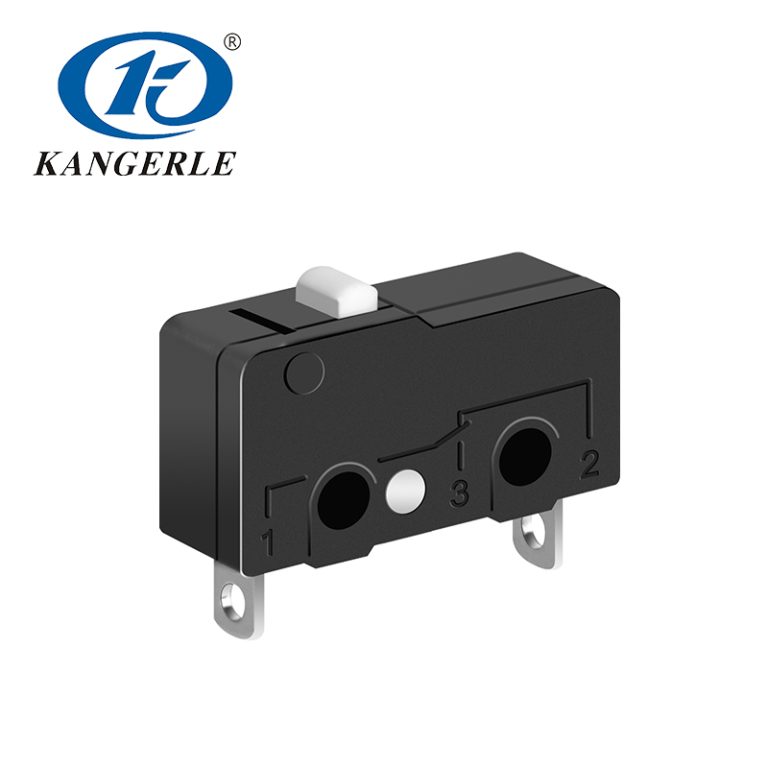
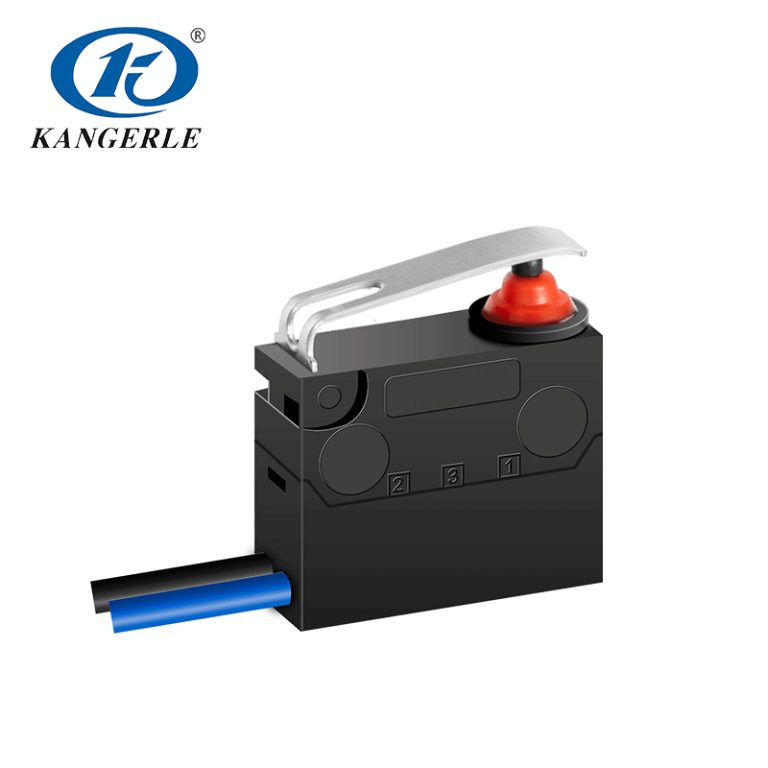
In the realm of electronics and electrical systems, the terms “switch” and “micro switch” are frequently encountered. Although both serve similar purposes in controlling the flow of electricity, their differences lie in their size, mechanism, and application. Where your field is be it household appliances, industrial equipment, or automotive applications, understanding these differences is essential when choosing the right type of switch for your project. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental distinctions between switches and micro switches, which will help you make an informed decision.
What is a Switch?
A switch is an electrical device used to connect or disconnect a circuit, thereby controlling the flow of electrical current. By pressing the switch, users can either allow or interrupt the electrical flow, depending on whether the circuit is in an “on” or “off” situation. Switches come in various sizes and configurations, offering different mechanisms for operation, ranging from manual toggles to automatic sensors.
Common types of switches include toggle switches, rocker switches, push-button switches, and slide switches. The size, design, and operation of a switch can vary significantly depending on the intended application, ranging from large industrial systems to small household devices.
Ordinary Types of Switches
Here are some common types of switches you might encounter:
1. Toggle Switches
These switchescan be operated by hand and typically feature a lever that can be toggled between two positions, allowing for on/off control.They are often used in household electrical systems.
2. Rocker Switches
They feature a rocker mechanism that can flip up or down to control power. These switches are often used in automotive or appliance applications.
3. Push-Button Switches
Found in everyday electronics such as remote controls or light switches, push-button switches function with a simple push to turn a device on or off.
4. Slide Switches
These switches work by sliding a button back and forth to control a circuit. They are commonly found inhome appliances like fans.
Application of Standard Switches
Standard switches are widely used across various industries and applications. Whether in lighting systems, home appliances, industrial machinery, or office equipment, switches serve as the basic control mechanism for regulating electrical flow. They are fundamental to user interaction with electrical systems.
Home Appliances: From refrigerators to microwaves, toggle and push-button switches control the operation of everyday household devices.
Industrial Equipment: Heavy machinery often uses large, robust switches to handle high-voltage systems.
Automotive Systems: Toggle and rocker switches are often used in cars for functions like turning on lights or controlling wipers.
Consumer Electronics: In devices such as laptops and TVs, switches control power, volume, and input options.
Basic introduction to a Micro Switch
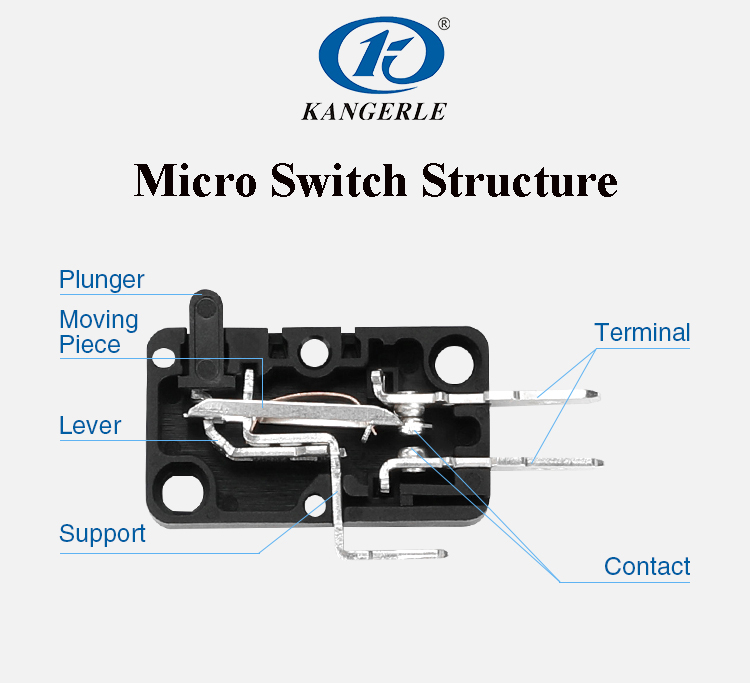
A micro switch, also known as a snap-action switch, is a specialized type of switch designed to operate under minimal force. These switches are commonly used in applications that require high sensitivity and precision, with an operation travel of only a few millimeters. Micro switches are typically characterized by their small size and a fast, reliable action that activates the switch once the actuator reaches a specific point.
When pressed, a micro switch “snaps” into place, triggering an electrical response. This snap-action mechanism is what makes micro switches ideal for sensitive applications where small amounts of physical force can trigger an electrical response. Micro switches are often used in situations that demand high reliability and precision in controlling electrical systems.
Common Types of Micro Switches

Micro switches come in various configurations, each tailored for specific applications:
1. Standard Micro Switches
– SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw): These are the most common micro switches, offering three terminals—one common terminal, one normally open (NO) terminal, and one normally closed (NC) terminal. They allow for both high and low circuits.
– DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw): Similar to SPDT, but with an additional set of terminals, allowing two circuits to be switched at once.
2. Sub-Miniature Micro Switches
– Smaller than standard micro switches, these are used in compact devices like toys, medical devices, and electronics. They offer the same high precision and sensitivity but in a smaller package.
3. Miniature and Ultra-Miniature Micro Switches
– Extremely small, these switches are used in very compact devices or in situations where space is at a premium, such as in hearing aids, cameras, or other small electronics.
4. Waterproof Micro Switches
– Designed with sealed casings to protect against water, dust, and debris. These are used in outdoor applications like lawn mowers, automotive systems, and other devices exposed to harsh environments.
Applications of Micro Switches
Micro switches are used in a broad range of applications due to their reliability and precision. Here are some common uses:
1. Home Appliances: Micro switches are frequently found in appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and microwaves. They ensure that these devices operate correctly by triggering specific actions, such as turning the machine on or off.
2. Automotive Applications: Micro switches, such as 12V micro switches, play a critical role in automotive systems. They are used in functions such as controlling lights, seat adjustments, and power windows.
3. Industrial Machinery: In industrial applications, micro switches are used in limit switches, door interlocks, and emergency stop systems. Their high reliability ensures the safe operation of machines.
4. Consumer Electronics: Micro switches are often used in buttons, keypads, and remote controls for electronic devices, offering users a tactile response.
5. Medical Equipment: Micro switches are used in medical devices such as blood pressure monitors, infusion pumps, and diagnostic equipment to ensure reliable operation in critical settings.
Differences Between a Switch and a Micro Switch
While both switches and micro switches are used to control electrical circuits, the key differences lie in their size, sensitivity, and mechanism of operation.
1. Size and Compactness: Micro switches are significantly smaller than standard switches. Their compact size allows them to be used in tight spaces where larger switches would be impractical.
2. Mechanism: Micro switches feature a snap-action mechanism that activates the switch with minimal force. In contrast, standard switches may require more force to operate, and their action may not be as precise.
3. Precision and Sensitivity: Micro switches are designed for precise operation with very little physical force. They are often used in applications that require highly sensitive, accurate, and reliable switching. Standard switches, on the other hand, are more general-purpose and are often used in less sensitive applications.
4. Durability: Micro switches are known for their durability and ability to withstand high-cycle operations. While standard switches are also reliable, micro switches are specifically designed for high-frequency use in critical applications.
5. Voltage and Current Rating: While standard switches are available in various voltage and current ratings, micro switches are typically used in low-voltage, low-current applications. For example, 12V micro switches are commonly used in automotive systems.
6. Applications: Micro switches are more commonly used in precision devices and small electronics, while standard switches are found in a broader range of applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Option
When selecting between a standard switch and a micro switch, it’s crucial to consider the specific requirements of your application. If you need a small, precise, and highly sensitive switch that operates with minimal force, a micro switch might be the ideal choice. For more general-purpose applications where size and precision are not as critical, a standard switch may be sufficient.
Whether you are looking for a toggle micro switch for a simple on/off function or a 12-volt micro switch for an automotive project, understanding the characteristics of each type will ensure you make the right choice for your needs. Keep in mind the factors such as size, voltage rating, durability, and precision when selecting a switch to ensure optimal performance and reliability in your system.








